The term “Safety Culture” is widely used today to describe the behavioral patterns, habits, and practices related to occupational safety within an organization. It is generally believed that strengthening safety culture can significantly reduce workplace accidents.
Industries and companies with a long-standing focus on occupational safety often demonstrate positive effects on economic success, reputation, and employee loyalty. However, what defines a company-specific safety culture? Are there methods to transform this broad and abstract concept into a tailored strategy with measurable objectives and outcomes?
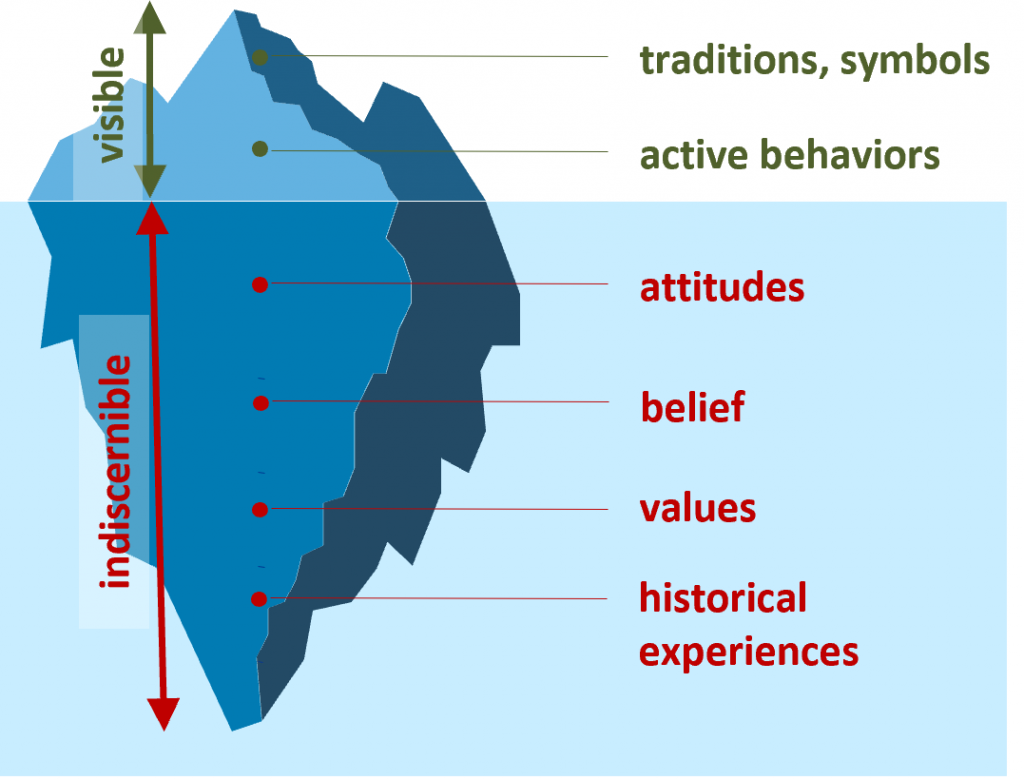
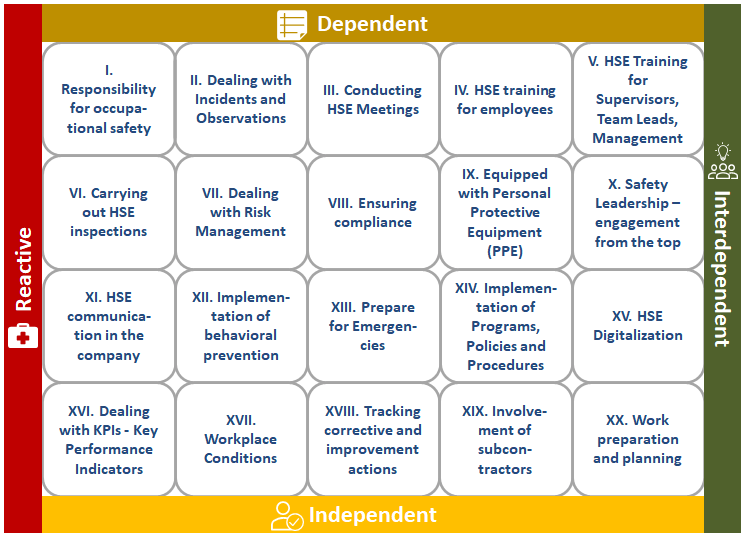
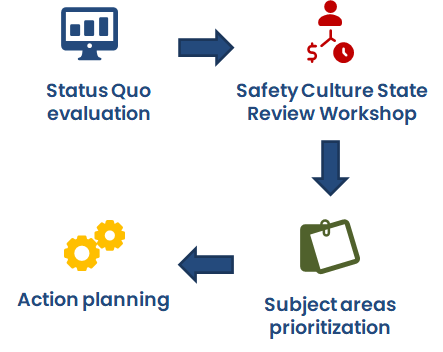
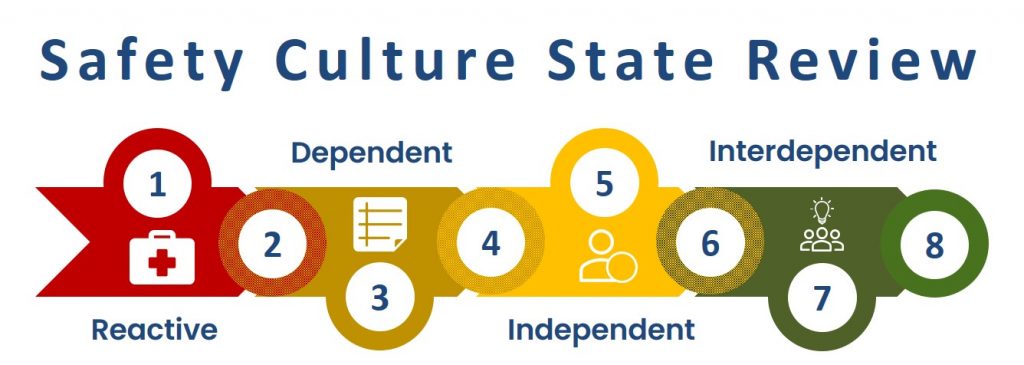
The Safety Culture State Review (SCSR) serves as a pivotal tool to identify both the current and desired future state of a company-specific safety culture. It provides safety professionals with a unified and accessible framework for engaging with senior leaders and operational management to set clear, measurable development goals. Importantly, the safety culture must align with the company’s unique characteristics, rather than being externally imposed. The SCSR applies Covey’s maturity levels — dependent, independent, and interdependent (Covey, S., The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. London, 2020) — while incorporating Bradley’s “reactive” level to connect safety culture maturity with occupational safety performance. This framework recognizes that accident rates often correlate with the existing internal safety culture shaped by unwritten rules, behaviors, values, and historical influences
.