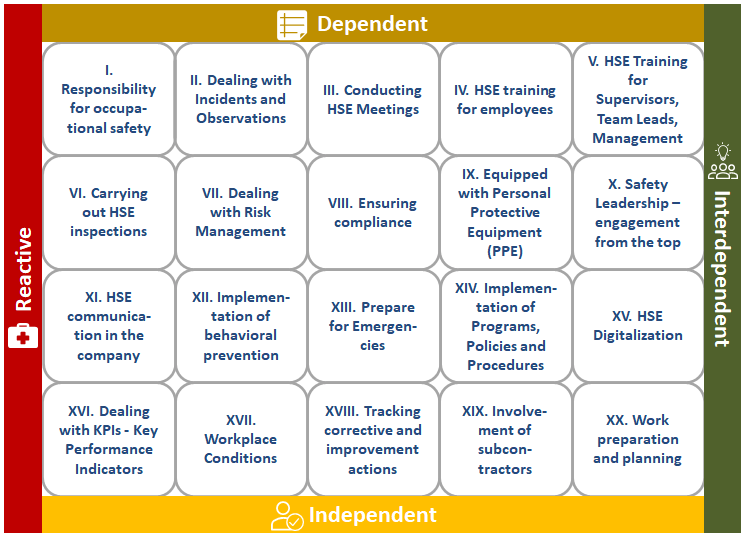
To evaluate a company’s safety culture, 20 key dimensions have been identified that significantly impact unconscious values, processes, and behavioral patterns related to occupational safety. These dimensions provide a structured approach to understanding and improving the cultural factors that influence safety performance.
Many of the 20 dimensions influencing a company’s safety culture are interconnected, meaning that improvements in one area often cascade to others. When choosing dimensions for enhancement, it is vital to align actions with the company’s processes and the targeted safety culture level. This ensures a manageable pace of change, avoiding overwhelming the organization. Internal cultural shifts (cultural transformation) require a long-term approach and cannot be effectively integrated into existing frameworks overnight. Planning and gradual implementation are key for sustainable change.
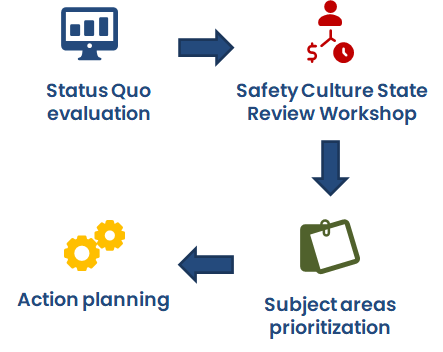
The method for assessing the status of a safety culture is detailed in the section on the Safety Culture State Review Index calculation. This section outlines the steps and metrics used to determine the current and desired state of a company’s safety culture, providing a structured approach to identify gaps and set improvement goals.
The 20 dimensions (I to XX) that have the greatest influence on a company-specific safety culture are defined in the following table. Each dimension is clickable, allowing you to explore its definition and cultural state implications. This approach provides actionable insights and facilitates meaningful discussions on developing a strong safety culture.
You can download the description of the maturity levels of the 20 dimensions as a PDF file via the following link
(Version SCSR v. 2.0 / 16.11.2025)
| SCSR - Dimensions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. Responsibility for Occupational Safety | II. Dealing with Incidents and Observations | III. Conducting Safety-Meetings | IV. Safety-Trainings for employees | V. Safety-Training for Supervisors, Team Leads, Management |
| VI. Carrying out Safety Inspections | VII. Dealing with Risk Management | VIII. Ensuring compliance | IX. Equipped with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | X. Safety Leadership (Leading by Example) |
| XI. Safety Communication in the Organisation | XII. Implementation of behavioral prevention | XIII. Prepare for Emergencies | XIV. Implementation of Safety Programs, Policies and Procedures | XV. Safety Digitalization |
| XVI. Dealing with KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) | XVII. Workplace Conditions | XVIII. Tracking corrective and improvement actions | XIX. Involvement of subcontractors | XX. Work preparation and planning |
The meaning of each dimension’s maturity level is shown below.
| (A) dependent | (B) independent | (C) interdependent | (D) reactive |
|---|---|---|---|