Key data
| Business: Power supply utility | Size: 2750 Employees + 1500 contractor employees | Safety performance 30% lower average accident rate compared on country level | Purpose Improvement driven by regional peer group |
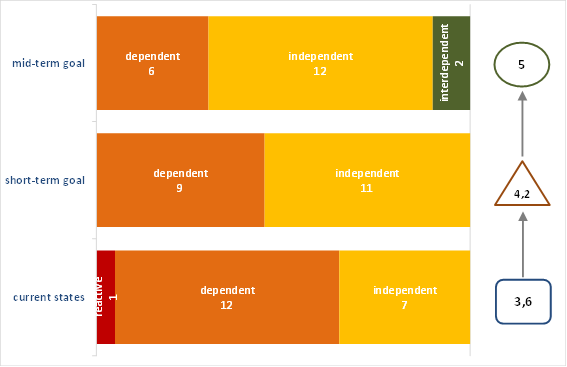
| Safety Culture Sate Review Presence workshop | Safety Culture Sate Review Index: 3,6 | Safety Culture Sate Review Short-term goal: 4,2 | Safety Culture Sate Review Mid-term goal: 5 |
Case Study: Defining Leading Cultural Indicators for Safety Improvement
This case study demonstrates how the results of a Safety Culture State Review workshop can be analyzed and how appropriate measures can be defined in collaboration with the workshop participants. The review results are available immediately during the workshop.
In this case, a new approach for defining leading cultural indicators is introduced. These indicators will enable the company to track the cultural change process and assess its impact on safety performance over time.
The case
The company is one of the leading organizations involved in the implementation of the country’s energy transition. It currently employs more than 2,750 people, with an additional workforce of over 1,500 external employees.
Two years ago, the company decided to place greater emphasis on cultural aspects to improve safety performance and, for the first time, initiated a review of its existing safety measures.
At present, the company records only accidents involving its own employees, as required by local legislation. The company’s accident rate is significantly better than the national average. Over the years, it has achieved notable improvements in reducing workplace accidents.
To ensure compliance with legal requirements, the company employs an Occupational Safety Manager, responsible for overseeing risk assessments, accident reporting, inspections, employee training, and serving as the primary contact for authorities and clients.
For over 20 years, the company has maintained a quality and environmental management system in accordance with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards.
Due to the ongoing energy transition, the company has been assigned new areas of responsibility that present significantly higher risk potential. Additionally, the company now faces international competition in these newly acquired business areas.
The Safety Culture State Review Workshop
To address these challenges, a Safety Culture State Review was conducted in the form of an in-person workshop with 25 managerial participants, moderated by the internal Safety Manager.
The workshop was structured into four key sections:
a) The importance of safety culture in improving safety performance
b) Safety Culture State Review Survey – evaluation of 20 dimensions by the participants
c) Presentation of the results
d) Definition of specific measures to enhance the company’s safety culture
By implementing this structured approach, the company aims to integrate cultural indicators into its safety management strategy, ensuring continuous improvement and long-term sustainability in workplace safety.