Why?
Dealing with Incidents is one of the main tasks of any safety professional and is listed in every job description available worldwide. However, there are only a few described procedures available to conduct in-depth investigations, so that it ultimately depends on the experience of a safety professional as to how and to what extent incident investigations are carried out in companies. In larger organisations there are sometimes guidelines and these are supported by the introduction of IT tools. Nevertheless, the question arises, how incident investigations are conducted holistically and whether the respective process also suits your company. But in case incident investigations are done properly (including observations), they represent an incredible pot of gold for a learning organization!
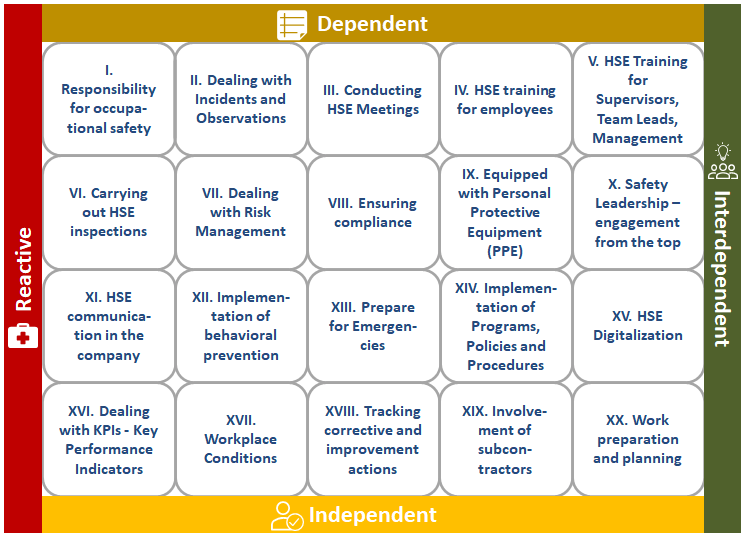
The meaning of the four states
 | dependent – Accident investigations are carried out sporadically for all classes of incidents; there is no systematic follow-up of measures; no systematic approach for observations reporting |
 | independent – Accident investigations are carried out systematically for all classes of incidents, there is a systematic approach for follow-up of measures and analysis of the incidents. Incidents are communicated within the company. Employees are encouraged to report observations |
 | interdependent – Investigations are carried out both in the case of incidents and observations; both are systematically analyzed and communicated within the company. Teams taking ownership for incident investigations; observation reporting is a fundamental element of cont. improvement |
 | reactive – Accident investigations are only carried out in the event of serious incidents, there is no systematic investigation approach and follow-up of measures and analysis of incidents |
How?
To initiate a discussion on this subject area the following key questions might be helpful for support:
Incident Investigations
- Do you have a structured process for investigating incidents and determining actions?
- Are the causes of incidents analyzed across departments and reported to management?
- Are managers and HSE specialists trained in the application of the investigation process?
- Are the results of incident investigations communicated within the organization?
- Do the specified measures often only include the affected employee (“induction to be carried out”), or are structural deficits addressed?
- Is the investigation process introduced adapted to company needs, or only imposed “from outside” (IT tool driven, bureaucratic)?