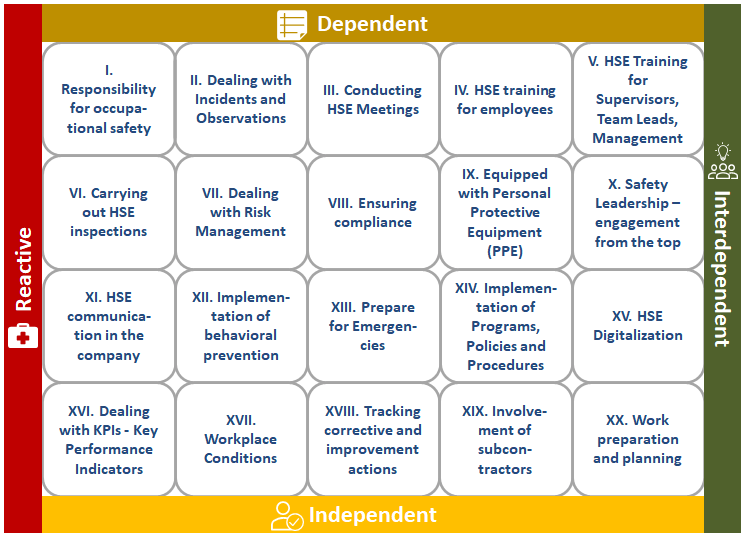
Why
Conducting inspections is a fundamental element of a company’s safety culture. Specialists check whether internally defined standards and processes are being adhered to in the respective area. However, there are significant differences in the way the inspections are carried out. On the one hand, these are only carried out to meet the local legal requirements, on the other hand, to learn from the respective ‘complaints’ and to continuously improve. In order to support this process of the learning organization, additional tools are required, such as a system for recording the inspections, for tracking the measures and recommendations as well as for the systematic evaluation of the ‘complaints’.
Another important aspect is whether the inspections are carried out on the initiative of the HSE department to document compliance with legal requirements, or whether the team leads and employees take the initiative and ask for support from the relevant professionals to improve.
The meaning of the four states
The characteristics of the four states can be described for this subject area as follows:
 | dependent – HSE inspections are planned and executed by HSE specialists as required, no systematically follow up on measures |
 | independent – HSE inspections are planned and executed systematically, risks are evaluated and measures are tracked. Inspections are regularly analyzed and communicated; team leads are involved in inspections planning and execution |
 | interdependent – Local teams request HSE specialists to carry out additional inspections to improve work processes; potential for improvement is actively communicated in the team; team members are actively participating in inspection execution and carrying out self-inspections |
 | reactive – No HSE inspections are carried out except those that are legally required |